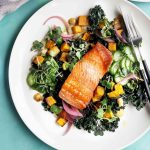Inflammation may be a health buzzword, but an anti-inflammatory diet is more than a trend—it can help you live a healthy life and age well. Inflammation gone wild can wreak havoc on the body and lead to chronic illness, such as heart disease and type 2 diabetes. An anti-inflammatory diet is one filled with nutrient-dense food from each of the macronutrients, carbs, fats, and yes, proteins. Here are four anti-inflammatory proteins we invite you to eat regularly to reduce the risk of chronic disease and feel your best.
1. Beans
Whether you prefer black, kidney, white, cannellini, lima or pinto beans, beans are a top anti-inflammatory protein. For one, the pigments in darker or colored beans provide anti-inflammatory antioxidant compounds that may help play a role in the prevention of cancer, heart disease, obesity and diabetes, according to a 2021 review published in Nutrients.
What’s more, beans are also packed with fiber, including a specific type of fiber—known as resistant starch—that can benefit your gut health, notes a 2022 study in the journal Nutrients. That starch provides food for good gut bacteria to promote a healthy microbiome, which may also lessen inflammation, adds Nancy Mazarin, M.S., RD, CDN, a dietitian in Long Island, New York, who counsels on weight management and medical nutrition therapy. Consider whipping up our Slow-Cooker Baked Beans for immune-fighting benefits.
2. Fatty Fish
Fatty fish, such as salmon, tuna and mackerel, are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, a type of fat with anti-inflammatory properties, says Mazarin. One meta-analysis, published in the journal Nutrients in 2020, examined the relationship between fish consumption and heart disease. With a total of 27 studies in the analysis, the authors concluded that each additional 20 grams of fish eaten per day (less than 1 ounce) was associated with a 4% lower risk of developing or dying from heart disease. That said, the authors believe that eating two ounces per day is ideal for reaping these benefits.
Why is fish so good for your health? Omega-3s improve heart and blood vessel function—and they’re anti-inflammatory, too, say researchers. Fish is also packed with vitamin D and selenium, nutrients that have additional antioxidant and anti-inflammatory benefits. That means that eating fish may provide more benefits than simply taking an omega-3 supplement. When it comes to choosing omega-3-rich seafood on your plate, “the fattier the fish, the better,” says Mazarin. If you do not eat fish, plant sources of omega-3s include flaxseeds and chia seeds. What better way to reap these benefits than with these easy-to-make Salmon Tacos with Pineapple Salsa?
3. Lentils
Lentils are packed with polyphenols, plant compounds that have antioxidant properties that, in part, can help reduce inflammation. Consuming them may be linked to a decreased risk of diabetes, obesity, cancer and heart disease, according to a 2022 review in the journal Pharmaceuticals. Like beans, lentils also have prebiotic fiber to promote a healthy gut. In addition, fiber may play a direct role in reducing chronic inflammation and promoting a healthy weight, which can also keep inflammation at bay, per 2023 research in Advances in Nutrition. Not sure where to start? Try our delicious Braised Black Lentil & Quinoa Bowls.
4. Nuts
Like beans, nuts also have anti-inflammatory properties, says Mazarin. Good things tend to happen when you eat nuts every day. Nuts, such as almonds and walnuts, have been found to decrease inflammation, per a 2023 review in the journal Nutrients. The authors say that nuts are packed with compounds like unsaturated fatty acids, vitamin E, selenium, copper, fiber and antioxidants that, alone and together, help counteract damaging oxidative stress and lessen inflammation. Additionally, nuts have as much protein as fish, eggs or meat. One ounce of almonds, for example (around 23 pieces), offers 6 grams of protein, the same as one large egg. Sprinkle your favorite nuts on a salad, oatmeal or yogurt bowl, or grab a handful as a snack to get in some extra protein.
What Is an Anti-Inflammatory Diet?
“An anti-inflammatory style of eating is very important. Inflammation is a significant contributing factor in the development of chronic medical conditions,” says Mazarin.
That said, it’s important to clarify the different types of inflammation. Acute inflammation, the short-term inflammation that happens as the result of, say, scraping your knee or getting sick with a cold, is a healthy and normal body response. It’s chronic inflammation that’s so insidious. “We are sending out inflammatory cells when we are not injured or sick,” says Mazarin. As a result, diseases such as arthritis, heart disease and diabetes are all linked to inflammation. “We want to squelch the fire of chronic inflammation,” she says.
The types of eating patterns that are associated with less risk of disease also happen to be more anti-inflammatory, such as the Mediterranean diet, DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) and MIND diet. While these aren’t completely plant-based, they promote consuming more plant-based foods such as fruits and vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts and seeds. However, just because they are more plant-forward doesn’t mean you have to skimp on protein or even animal-based sources. In fact, animal-protein foods also have a place in these diets.
The Bottom Line
While there are many anti-inflammatory foods you can add to your rotation, focus on beans, fatty fish, lentils and nuts if you’re looking to add high-protein sources, too. Not only are these foods versatile, the are filled with essential vitamins, minerals and antioxidants that may reduce your risk of chronic disease. Along with a diet filled with nutrient-dense fruits, vegetables, whole grains and dairy, these inflammation-flighting proteins all fit into a nutritious and balanced diet.